Question.
The values of current, I, flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference, $V$, across the resistor are given below :
I (ampere): $\quad 0.5 \quad 1.0 \quad 2.0 \quad 3.0 \quad 4.0$
$\begin{array}{lllllll}\text { V (volt) } & : & 1.6 & 3.4 & 6.7 & 10.2 & 13.2\end{array}$
Plot a graph between $\mathrm{V}$ and $\mathrm{I}$ and calculate the resistance of the resistor.
The values of current, I, flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference, $V$, across the resistor are given below :
I (ampere): $\quad 0.5 \quad 1.0 \quad 2.0 \quad 3.0 \quad 4.0$
$\begin{array}{lllllll}\text { V (volt) } & : & 1.6 & 3.4 & 6.7 & 10.2 & 13.2\end{array}$
Plot a graph between $\mathrm{V}$ and $\mathrm{I}$ and calculate the resistance of the resistor.
solution:
The V-I graph is as shown in fig.
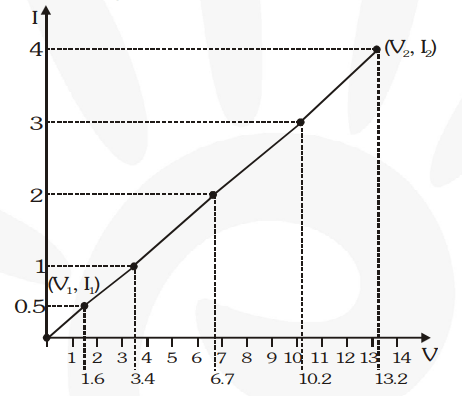
Here, the I – V graph is almost straight. The resistance of the resistor can be calculated as given
below, $\mathrm{R}=\frac{\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}}{\mathrm{I}_{2}-\mathrm{I}_{1}}=\frac{13.2-1.6}{4-0.5}=\frac{11.6}{3.5}=\mathbf{3 . 3} \mathbf{\Omega}$
The V-I graph is as shown in fig.

Here, the I – V graph is almost straight. The resistance of the resistor can be calculated as given
below, $\mathrm{R}=\frac{\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}}{\mathrm{I}_{2}-\mathrm{I}_{1}}=\frac{13.2-1.6}{4-0.5}=\frac{11.6}{3.5}=\mathbf{3 . 3} \mathbf{\Omega}$
