The points A (2, 9), B (a, 5), C (5, 5) are the vertices of a triangle ABC right angled at B. Find the value of 'a' and hence the area of ΔABC.
It is given that ABC is a right angled triangle.![]() .Vertices of triangle are
.Vertices of triangle are
A( 2,9 ), B( a,5 ), C( 5, 5 ).
We have to find the value of a and area of the triangle.
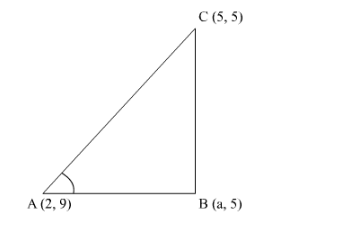
![]() is a right angled triangle.
is a right angled triangle.
We know that length of a line with coordinates of end points $\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right)$ and $\left(x_{2}, y_{2}\right)$
$=\sqrt{\left(x_{2}-x_{1}\right)^{2}+\left(y_{2}-y_{1}\right)^{2}}$
Hence in $\triangle A B C$
$A B=\sqrt{(a-2)^{2}+(5-9)^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{a^{2}-4 a+4+16}$
$=\sqrt{a^{2}-4 a+20}$.......(1)
$B C=\sqrt{(a-5)^{2}+(5-5)^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{a^{2}-10 a+25}$
$=\sqrt{a^{2}-10 a+25} \ldots \ldots(2)$
$A C=\sqrt{(5-2)^{2}+(5-9)^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{9+16}$
$=\sqrt{25}$
$=5$
Therefore, applying Pythagoras Theorem to right ![]()
$A B^{2}+B C^{2}=A C^{2}$
$\left(\sqrt{a^{2}-4 a+20}\right)^{2}+\left(\sqrt{a^{2}-10 a+25}\right)^{2}=5^{2}$
$a^{2}-4 a+20-a^{2}-10 a+25=25$
$2 a^{2}-14 a+20=0$
$2\left(a^{2}-7 a+10\right)=0$
$a^{2}-7 a+10=0$
$a^{2}-5 a-2 a+10=0$
$a(a-5)+2(a-5)=0$
$(a-5)(a-2)=0$
$a=5,2$
$a \neq 5$ because it will make the coordinates of $B$ and $C$ same
Therefore $a=2$
Putting a = 2 in (1) and (2)
$A B=\sqrt{2^{2}-4 \times 2+20}$
$=\sqrt{16}$
$=4$
$B C=\sqrt{a^{2}-10 a+25}$
$=\sqrt{2^{2}-10 \times 2+25}$
$=\sqrt{9}$
$=3$
Area of right angled $\triangle A B C=\frac{1}{2} \times A B \times B C$
$=\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 3$
$=6$
