$\int_{0}^{\pi} \log (1+\cos x) d x$
Let $I=\int_{0}^{\pi} \log (1+\cos x) d x$ (1)
$\Rightarrow I=\int_{1}^{\pi} \log (1+\cos (\pi-x)) d x$ 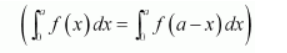
$\Rightarrow I=\int_{0}^{\pi}\log (1-\cos x) d x$ ...(2)
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
$2 I=\int_{0}^{\pi}\{\log (1+\cos x)+\log (1-\cos x)\} d x$
$\Rightarrow 2 I=\int_{0}^{\pi} \log \left(1-\cos ^{2} x\right) d x$
$\Rightarrow 2 I=\int_{0}^{\pi} \log \sin ^{2} x d x$
$\Rightarrow 2 I=2 \int_{0}^{\pi} \log \sin x d x$
$\Rightarrow I=\int_{0}^{\pi} \log \sin x d x$ ...(3)
$\sin (\pi-x)=\sin x$
$\therefore I=2 \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log \sin x d x$ ...(4)
$\Rightarrow I=2 \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right) d x=2 \int_{1}^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log \cos x d x$ ...(5)
Adding (4) and (5), we obtain
$2 I=2 \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}(\log \sin x+\log \cos x) d x$
$\Rightarrow I=\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}(\log \sin x+\log \cos x+\log 2-\log 2) d x$
$\Rightarrow I=\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}(\log 2 \sin x \cos x-\log 2) d x$
$\Rightarrow I=\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log \sin 2 x d x-\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \log 2 d x$
Let $2 x=t \Rightarrow 2 d x=d t$
When $x=0, t=0$
and when $x=\frac{\pi}{2}, t=\pi$
$\therefore I=\frac{1}{2} \int_{0}^{\pi} \log \sin t \mathrm{~d} t-\frac{\pi}{2} \log 2$
$\Rightarrow I=\frac{I}{2}-\frac{\pi}{2} \log 2 \quad[$ from 3$]$
$\Rightarrow \frac{I}{2}=-\frac{\pi}{2} \log 2$
$\Rightarrow I=-\pi \log 2$
