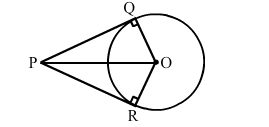
O is the centre of a circle of radius 5 cm. At a distance of 13 cm from O, a point P is taken. From this point, two tangents PQ and PR are drawn to the circle. Then, the area of quadrilateral PQOR is
(a) 60 cm2
(b) 32.5 cm2
(c) 65 cm2
(d) 30 cm2
(a) 60 cm2
Given,
$O Q=O R=5 \mathrm{~cm}, O P=13 \mathrm{~cm} .$
$\angle O Q P=\angle O R P=90^{\circ}$ (T angents drawn from an external point are perpendicular
to the radius at the point of contact)
From right - angled $\triangle P O Q$ :
$P Q^{2}=\left(O P^{2}-O Q^{2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow P Q^{2}=13^{2}-5^{2}$
$\Rightarrow P Q^{2}=169-25$
$\Rightarrow P Q^{2}=144$
$\Rightarrow P Q=\sqrt{144}$
$\Rightarrow P Q=12 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\therefore a r(\triangle O Q P)=\frac{1}{2} \times P Q \times O Q$
$\Rightarrow a r(\triangle O Q P)=\left(\frac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 5\right) \mathrm{cm}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \operatorname{ar}(\triangle O Q P)=30 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
Similarly, $a r(\triangle O R P)=30 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
$\therefore \operatorname{ar}($ quad. PQOR $)=(30+30) \mathrm{cm}^{2}=60 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
