In the given figure, ∆ABC is an obtuse triangle, obtuse-angles at B. If AD ⊥ CB, Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2BC ⋅ BD.
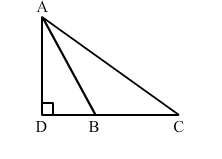
Applying Pythagoras theorem in right-angled triangle ADC, we get:
$A C^{2}=A D^{2}+D C^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A C^{2}-D C^{2}=A D^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A D^{2}=A C^{2}-D C^{2}$ ..........(1)
Applying Pythagoras theorem in right-angled triangle ADB, we get:
$A B^{2}=A D^{2}+D B^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A B^{2}-D B^{2}=A D^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A D^{2}=A B^{2}-D B^{2} \quad \ldots(2)$
From equation $(1)$ and $(2)$, we have :
$A C^{2}-D C^{2}=A B^{2}-D B^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A C^{2}=A B^{2}+D C^{2}-D B^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A C^{2}=A B^{2}+(D B+B C)^{2}-D B^{2} \quad(\because D B+B C=D C)$
$\Rightarrow A C^{2}=A B^{2}+D B^{2}+B C^{2}+2 D B \cdot B C-D B^{2}$
$\Rightarrow A C^{2}=A B^{2}+B C^{2}+2 B C \cdot B D$
This completes the proof.
