In an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC and BD ⊥ AC. Prove that BD2 − CD2 = 2CD.AD.
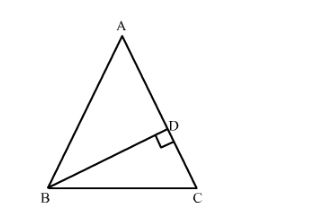
Given: ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC and BD ⊥ AC.
To prove: BD2 − CD2 = 2CD.AD
Proof: In right ∆ADB,
$\mathrm{AB}^{2}=\mathrm{AD}^{2}+\mathrm{BD}^{2}$ (Pythagoras Theorem)
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{AC}^{2}=\mathrm{AD}^{2}+\mathrm{BD}^{2} \quad(\mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{AC})$
$\Rightarrow(\mathrm{AD}+\mathrm{CD})^{2}=\mathrm{AD}^{2}+\mathrm{BD}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{AD}^{2}+\mathrm{CD}^{2}+2 \mathrm{AD} \cdot \mathrm{CD}=\mathrm{AD}^{2}+\mathrm{BD}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{BD}^{2}-\mathrm{CD}^{2}=2 \mathrm{AD} \cdot \mathrm{CD}$ (Hence Proved)
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
