Question:
If the value of the integral $\int_{0}^{5} \frac{x+[x]}{e^{x-[x]}} d x=\alpha e^{-1}+\beta$,where $\alpha, \beta \in \mathbf{R}, 5 \alpha+6 \beta=0$, and $[x]$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $x$; then the value of $(\alpha+\beta)^{2}$ is equal to:
Correct Option: , 2
Solution:
$I=\int_{0}^{5} \frac{x+[x]}{e^{x-[x]}} d x$
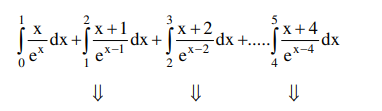
$\int_{0}^{1} \frac{t+2}{e^{t}} d t+\int_{0}^{1} \frac{z+4}{e^{z}} d z+\ldots \ldots+\int_{0}^{1} \frac{y+8}{e^{y}} d x$
$\Rightarrow \int_{0}^{5} \frac{5 x+20}{e^{x}} d t=5 \int_{0}^{1} \frac{x+4}{e^{x}} d x$
$\Rightarrow 5 \int_{0}^{1}(x+4) e^{-x} d x$
$\left.\Rightarrow 5 e^{-x}(-x-5)\right|_{0} ^{1} \Rightarrow-\frac{30}{e}+25$
$\alpha=-30$
$\beta=25 \Rightarrow 5 \alpha+6 \beta=0$
$(\alpha+\beta)^{2}=5^{2}=25$
