If the tangent to the curve $y=x^{3}+a x+b$ at $(1,-6)$ is parallel to the line $x-y+5=0$, find $a$ and $b$
Given:
The Slope of the tangent to the curve $y=x^{3}+a x+b$ at
$(1,-6)$
First, we will find The Slope of tangent
$y=x^{3}+a x+b$
$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}\left(\mathrm{x}^{3}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}(\mathrm{ax})+\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}(\mathrm{b})$
$\Rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=3 x^{3}-1+a\left(\frac{d x}{d x}\right)+0$
$\Rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=3 x^{2}+a$
The Slope of the tangent to the curve $y=x^{3}+a x+b$ at
$(1,-6)$ is
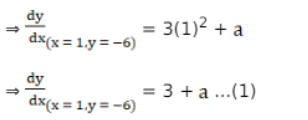
The given line is $x-y+5=0$
$y=x+5$ is the form of equation of a straight line $y=m x+c$, where $m$ is the The Slope of the line.
so the The Slope of the line is $y=1 \times x+5$
so The Slope is $1 \ldots . .(2)$
Also the point $(1,-6)$ lie on the tangent, so
$x=1 \& y=-6$ satisfies the equation, $y=x^{3}+a x+b$
i.e, $-6=1^{3}+a \times 1+b$
$\Rightarrow-6=1+a+b$
$\Rightarrow a+b=-7 \ldots(3)$
Since, the tangent is parallel to the line, from $(1) \&(2)$
Hence,
$3+a=1$
$\Rightarrow a=-2$
From (3)
$a+b=-7$
$\Rightarrow-2+b=-7$
$\Rightarrow b=-5$
$a+b=-7$
$\Rightarrow-2+b=-7$
$\Rightarrow b=-5$
So the value is $a=-2 \& b=-5$
