If the system of equations has infinitely many solutions, then
$2 x+3 y=7$
$(a+b) x+(2 a-b) y=21$
(a) $a=1, b=5$
(b) $a=5, b=1$
(c) $a=-1, b=5$
(d) $a=5, b=-1$
The given systems of equations are
$2 x+3 y=7$
$(a+b) x+(2 a-b) y=21$
For the equations to have infinite number of solutions, $\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}=\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}$
Here $a_{1}=2, a_{2}=(a+b), b_{1}=3, b_{2}=2 a-b, c_{1}=7, c_{2}=21$
$\frac{2}{a+b}=\frac{3}{2 a-b}=\frac{7}{21}$
Let us take $\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}$
$\frac{2}{a+b}=\frac{3}{2 a-b}$
By cross multiplication we get,
$2(2 a-b)=3(a+b)$
$4 a-2 b=3 a+3 b$
$4 a-3 a=3 b+2 b$
$a=5 b \cdots(i)$
Now take $\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}=\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}$
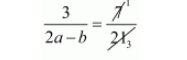
$\frac{3}{2 a-b}=\frac{1}{3}$
By cross multiplication we get,
$3 \times 3=1 \times 2 a-b$
$9=2 a-b \cdots(i i)$
Substitute $a=5 b$ in the above equation
$9=2 \times 5 b-b$
$9=10 b-b$
$9=9 b$
$\frac{9}{9}=b$
$1=b$
Substitute $b=1$ in equation $(i)$ we get, $a=5 b$
$a=5 \times 1$
$a=5$
Therefore $a=5$ and $b=1$.
Hence, the correct choice is $b$.
