Question:
If the bisector of an angle of a triangle bisects the opposite side, then the triangle is
(a) scalene
(b) equilateral
(c) isosceles
(d) right-angled
Solution:
(c) isosceles
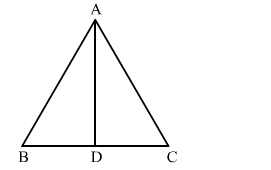
Let AD be the angle bisector of angle A in triangle ABC.
Applying angle bisector theorem, we get:
$\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{B D}{D C}$
It is given that AD bisects BC.
Therefore, BD = DC
$\Rightarrow \frac{A B}{A C}=1$
$\Rightarrow A B=A C$
Therefore, the triangle is isosceles.
