Question:
If $\alpha, \beta$ are the zeros of the polynomial $p(x)=4 x^{2}+3 x+7$, then $\frac{1}{\alpha}+\frac{1}{\beta}$ is equal to
(a) $\frac{7}{3}$
(b) $-\frac{7}{3}$
(c) $\frac{3}{7}$
(d) $-\frac{3}{7}$
Solution:
Since $\alpha$ and $\beta$ are the zeros of the quadratic polynomial $p(x)=4 x^{2}+3 x+7$
$\alpha+\beta=\frac{-\text { Coefficient of } x}{\text { Coefficient of } x^{2}}$
$=\frac{-3}{4}$
$\alpha \beta=\frac{\text { Constant term }}{\text { Coefficient of } x^{2}}$
$=\frac{7}{4}$
We have
$=\frac{1}{\alpha}+\frac{1}{\beta}$
$=\frac{\beta+\alpha}{\alpha \beta}$
$=\frac{-3}{\frac{4}{\frac{7}{4}}}$
$=\frac{-3}{4} \times \frac{4}{7}$
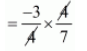
$=\frac{-3}{7}$
The value of $\frac{1}{\alpha}+\frac{1}{\beta}$ is $\frac{-3}{7}$.
Hence, the correct choice is (b)
