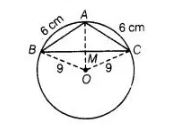
If an isosceles ΔABC in which AB = AC = 6 cm, is inscribed in a circle of radius 9 cm, find the area of the triangle.
In a circle, ΔABC is inscribed.
Join OB, OC and OA.
Conside $\triangle A B O$ and $\triangle A C O$
$A B=A C$ [given]
$B O=C O$ [radii of same circle]
$A O$ is common.
$\therefore$ $\triangle A B O \cong \triangle A C O$ [by SSS congruence rule]
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle 1=\angle 2$ [CPOT]
Now, in $\triangle A B M$ and $\triangle A C M$,
$A B=A C$ [given]
$\angle 1=\angle 2$ [proved above]
$A M$ is common.
$\therefore$ $\triangle A M B \cong \triangle A M C$ [by SAS congruence rule]
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle A M B=\angle A M C$ [CPCT]
Also, $\angle A M B+\angle A M C=180^{\circ}$ [linear pair]
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle A M B={ }^{\top} 90^{\circ}$
We know that a perpendicular from centre of circle bisects the chord. So. $O A$ is perpendicular bisector of $B C$.
Let $A M=x$, then $O M=9-x$ $[\because O A=$ radius $=9 \mathrm{~cm}]$
$A C^{2}=A M^{2}+M C^{2} \quad$ [by Pythagoras theorem]
i.e., (Hypotenuse) $^{2}=(\text { Base })^{2}+(\text { Perpendicular })^{2}$
$\Rightarrow$ $M C^{2}=6^{2}-x^{2}$ ....(1)
and in right $\triangle O M C, \quad O C^{2}=O M^{2}+M C^{2}$ [by Pythagoras theorem]
$\Rightarrow$ $M C^{2}=9^{2}-(9-x)^{2}$ ....(ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), $\quad 6^{2}-x^{2}=9^{2}-(9-x)^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \quad 36-x^{2}=81-\left(81+x^{2}-18 x\right)$
$\Rightarrow$$36=18 x \Rightarrow x=2$
$\therefore$ $A M=x=2$
In right angled $\triangle A B M$. $A B^{2}=B M^{2}+A M^{2}$ [by Pythagoras theorem]
$6^{2}=B M^{2}+2^{2}$
$\Rightarrow$ $B M^{2}=36-4=32$
$\therefore$ Area of $\triangle A B C=\frac{1}{2} \times$ Base $\times$ Height
$=\frac{1}{2} \times B C \times A M$
$=\frac{1}{2} \times 8 \sqrt{2} \times 2=8 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
Hence, the required area of $\triangle A B C$ is $B \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$.
