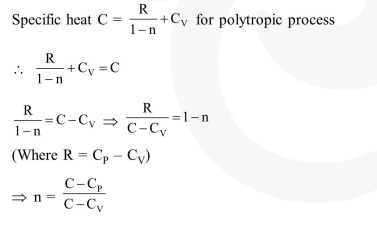
An ideal gas undergoes a quasi static, reversible process in which its molar heat capacity C remains constant.
Question:
An ideal gas undergoes a quasi static, reversible process in which its molar heat capacity C remains constant. If during this process the relation of pressure $\mathrm{P}$ and volume $\mathrm{V}$ is given by $\mathrm{PV}=$ constant, then $\mathrm{n}$ is given by (Here $\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{P}}$ and $\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{V}}$ are molar specific heat at constant pressure and constant volume, respectively) :-
Correct Option: , 3
Solution: