A random variable X has the following probability distribution.
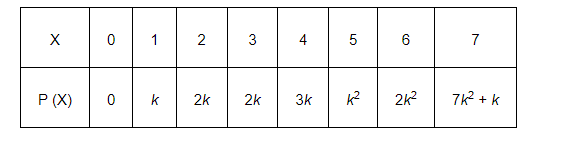
Determine
(i) $k$
(ii) $P(X<3)$
(iii) $P(X>6)$
(iv) $P(0
(i) It is known that the sum of probabilities of a probability distribution of random variables is one.
$\therefore 0+k+2 k+2 k+3 k+k^{2}+2 k^{2}+\left(7 k^{2}+k\right)=1$
$\Rightarrow 10 k^{2}+9 k-1=0$
$\Rightarrow(10 k-1)(k+1)=0$
$\Rightarrow k=-1, \frac{1}{10}$
k = − 1 is not possible as the probability of an event is never negative.
$\therefore k=\frac{1}{10}$
(ii) $P(X<3)=P(X=0)+P(X=1)+P(X=2)$
$=0+k+2 k$
$=3 k$
$=3 \times \frac{1}{10}$
$=\frac{3}{10}$
(iii) $P(X>6)=P(X=7)$
$=7 k^{2}+k$
$=7 \times\left(\frac{1}{10}\right)^{2}+\frac{1}{10}$
$=\frac{7}{100}+\frac{1}{10}$
$=\frac{17}{100}$
(iv) $P(0
$=k+2 k$
$=3 k$
$=3 \times \frac{1}{10}$
$=\frac{3}{10}$
