Neutral Point of Magnet - Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Physics Notes
JEE Mains & AdvancedA neutral point of Magnet is a point at which the resultant magnetic field is zero. In general, the neutral point is obtained when a horizontal component of the earth's field is balanced by the produced by the magnet. When the N pole of the magnet points South and the magnet in the magnetic meridian. When we plot the magnetic field of a bar magnet the curves obtained represent the superposition of magnetic fields due to bar magnet and earth.
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
DEFINITION
A neutral point in the magnetic field of a bar magnet is that point where the field due to the magnet is completely neutralized by the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field. At neutral point field due to bar magnet (B) is equal and opposite to horizontal component of earth's magnetic field $\left( B _{ H }\right) or \quad B = B _{ H }$
-
The neutral point when the north pole of a magnet is towards the geographical north of the earth.
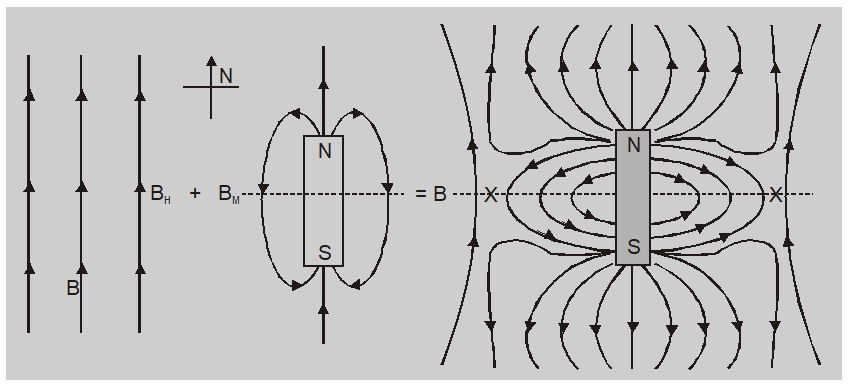
The neutral points $N_{1}$ and $N_{2}$ lie on the equatorial line. The magnetic field due to magnet at a neutral point is
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
$B =\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{ M }{\left( r ^{2}+\ell^{2}\right)^{\frac{3}{2}}}$
Where M is the magnetic dipole moment of the magnet, $2 l$is its length, and r is a distance of the neutral point.
At neutral point $B = B _{ H } \cdot \quad$ so $\quad \frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{ M }{\left( r ^{2}+\ell^{2}\right)^{\frac{3}{2}}}= B _{ H }$
For a small bar magnet $\left(\ell^{2}<< r ^{2}\right)$ then $\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{ M }{ r ^{3}}= B _{ H }$
-
Neutral point when south pole of a magnet is towards geographical north of earth.
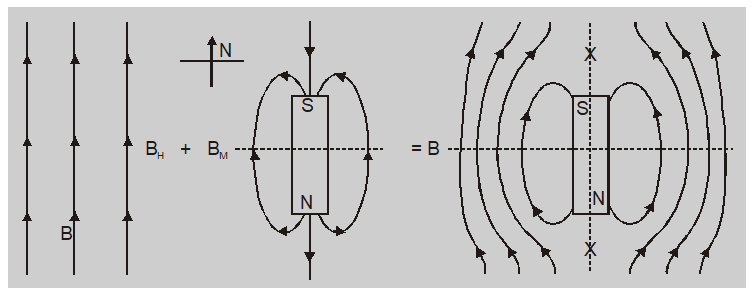
The neutral points $N_{1}$ and $N_{2}$ lie on the axial line of magnet. The magnetic field due to magnet
at neutral point is $B =\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 Mr }{\left( r ^{2}-\ell^{2}\right)^{2}}$
At neutral point $B =\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 Mr }{\left( r ^{2}-\ell^{2}\right)^{2}}$ so $\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 Mr }{\left( r ^{2}-\ell^{2}\right)^{2}}= B _{ H }$
For a small bar magnet $\left(\ell^{2}<< r ^{2}\right)$ then $\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi} \frac{2 M }{ r ^{3}}= B _{ H }$
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
Special Point
When a magnet is placed with its S pole towards north of earth neutral points lie on its axial line. If magnet is placed with its N pole towards north of earth neutral points lie on its equatorial line. So neutral points are displaced by $90^{\circ}$ on rotating magnet through $180^{\circ}$ In general if magnet is rotated by angle $\theta$ neutral point turn through an angle $\frac{\theta}{2}$
Neutral Point in Special Cases
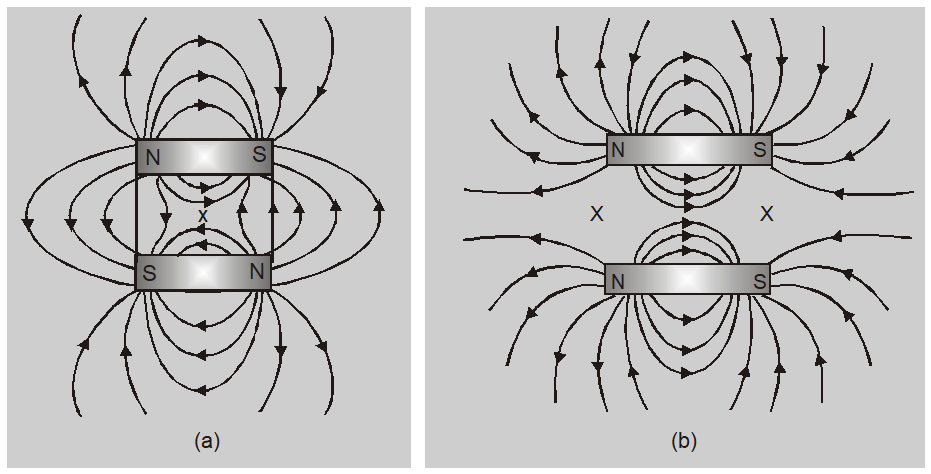
(a) If two bar magnets are placed with their axis parallel to each other and their opposite poles face each other then there is only one neutral point (x) on the perpendicular bisector of the axis equidistant from the two magnets.
(b) If two bar magnets are placed with their axis parallel to each other and their like poles face each other then there are two neutral points on a line equidistant from the axis of the magnets.
Also Read: Properties of Paramagnetic & Diamagnetic Materials
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
About eSaral At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
