JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions of Physics with Solutions are available at eSaral. Practicing JEE Advanced Previous Year Papers Questions of Physics will help the JEE aspirants in realizing the question pattern as well as help in analyzing weak & strong areas.
Simulator
Previous Years JEE Advanced Questions
Paragraph–1
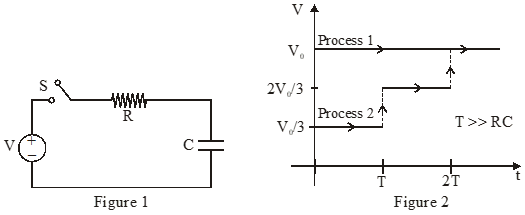
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage $\left.\mathrm{V}_{0} \text { (i.e., charging continues for time } \mathrm{T}>>\mathrm{RC}\right)$. In the process some dissipation $\left(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}\right)$ occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{c}}$.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to $\frac{\mathrm{v}_{0}}{3}$ and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to $\frac{2 v_{0}}{3}$ without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to $\mathrm{V}_{0}$ and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage $\mathrm{V}_{0}$ as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.
Q. At time t = 0, a battery of 10V is connected across points A and B in the given circuit. If the capacitors have no charge initially, at what time (in seconds) does the voltage across them become 4V?
[Take : $\ell \mathrm{n} 5=1.6, \ell \mathrm{n} 3$ = 1.1]
 [IIT-JEE 2010]
[IIT-JEE 2010]
 [IIT-JEE 2010]
[IIT-JEE 2010]
Ans. 2
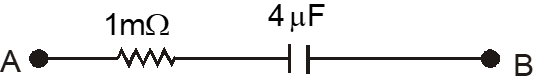 $Q=Q_{0}\left(1-e^{-t / R C}\right)$
$16 \mu \mathrm{Q}=40 \mu \mathrm{Q}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-1 / 4}\right)$
t = 2 sec
$Q=Q_{0}\left(1-e^{-t / R C}\right)$
$16 \mu \mathrm{Q}=40 \mu \mathrm{Q}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-1 / 4}\right)$
t = 2 sec
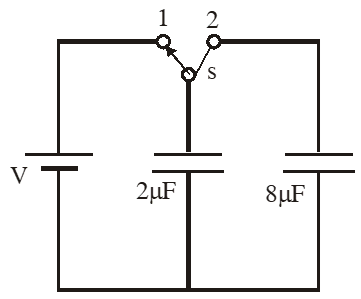
Q. A 2 $\mu \mathrm{F}$ capacitor is charged as shown in figure. The percentage of its stored energy dissipated after the switch S is turned to position 2 is
 (A) 0%
(B) 20%
(C) 75%
(D) 80%
[IIT-JEE 2011]
(A) 0%
(B) 20%
(C) 75%
(D) 80%
[IIT-JEE 2011]
 (A) 0%
(B) 20%
(C) 75%
(D) 80%
[IIT-JEE 2011]
(A) 0%
(B) 20%
(C) 75%
(D) 80%
[IIT-JEE 2011]
Ans. (D)

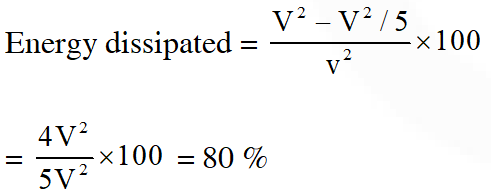


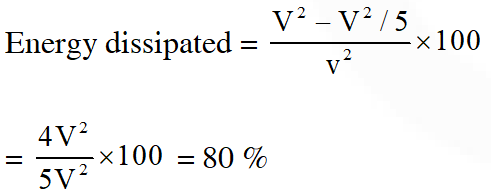
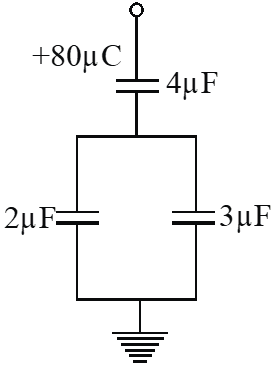
Q. In the given circuit, a charge of $+80 \mu C$ is given to the upper plate of the $4 \mu \mathrm{F}$ capacitor. Then in the steady state, the charge on the upper plate of the $3 \mu \mathrm{F}$ capacitor is -
 $(\mathrm{A})+32 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(B) $+40 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(C) $+48 \mu \mathrm{C}$
$(\mathrm{D})+80 \mu \mathrm{C}$
[IIT-JEE 2012]
$(\mathrm{A})+32 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(B) $+40 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(C) $+48 \mu \mathrm{C}$
$(\mathrm{D})+80 \mu \mathrm{C}$
[IIT-JEE 2012]
 $(\mathrm{A})+32 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(B) $+40 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(C) $+48 \mu \mathrm{C}$
$(\mathrm{D})+80 \mu \mathrm{C}$
[IIT-JEE 2012]
$(\mathrm{A})+32 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(B) $+40 \mu \mathrm{C}$
(C) $+48 \mu \mathrm{C}$
$(\mathrm{D})+80 \mu \mathrm{C}$
[IIT-JEE 2012]
Ans. (C)


Q. In the circuit shown in the figure, there are two parallel plate capacitors each of the capacitance C. The switch $\mathrm{S}_{1}$ is pressed first to fully charge the capacitor $\mathrm{C}_{1}$ and then released. The switch $\mathrm{S}_{2}$ is then pressed to charge the capacitor $\mathrm{C}_{2}$. After some time, $\mathrm{S}_{2}$ is released and then $\mathrm{S}_{3}$ is pressed, After some time,
 (A) the charge on the upper plate of $C_{1}$ is $2 C V_{0}$
(B) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{1}$ is $\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
(C) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $0 .$
(D) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $-\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
[IIT-JEE 2013]
(A) the charge on the upper plate of $C_{1}$ is $2 C V_{0}$
(B) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{1}$ is $\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
(C) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $0 .$
(D) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $-\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
[IIT-JEE 2013]
 (A) the charge on the upper plate of $C_{1}$ is $2 C V_{0}$
(B) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{1}$ is $\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
(C) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $0 .$
(D) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $-\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
[IIT-JEE 2013]
(A) the charge on the upper plate of $C_{1}$ is $2 C V_{0}$
(B) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{1}$ is $\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
(C) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $0 .$
(D) the charge on the upper plate of $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is $-\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
[IIT-JEE 2013]
Ans. (B,D)
Before $\mathrm{S}_{3}$ is pressed
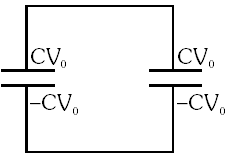 After $\mathrm{S}_{3}$ is pressed
After $\mathrm{S}_{3}$ is pressed

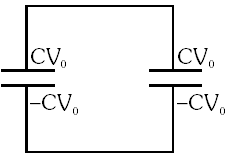 After $\mathrm{S}_{3}$ is pressed
After $\mathrm{S}_{3}$ is pressed

Q. A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K between its plates that covers 1/3 of the area of its plates, as shown in the figure. The total capacitance of the capacitor is C while that of the portion with dielectric in between is $\mathrm{C}_{1}$. When the capacitor is charged, the plate area covered by the dielectric gets charge $\mathrm{Q}_{1}$ and the rest of the area gets charge $Q_{2}$. The electric field in the dielectric is $\mathbf{E}_{1}$ and that in the other portion is $\mathrm{E}_{2}$. Choose the correct option/options, ignoring edge effects.
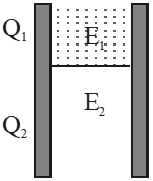 (A) $\frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
(B) $\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{E}_{2}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}}$
(C) $\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{3}{\mathrm{K}}$
(D) $\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{2+\mathrm{K}}{\mathrm{K}}$
[IIT-JEE 2014]
(A) $\frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
(B) $\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{E}_{2}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}}$
(C) $\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{3}{\mathrm{K}}$
(D) $\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{2+\mathrm{K}}{\mathrm{K}}$
[IIT-JEE 2014]
 (A) $\frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
(B) $\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{E}_{2}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}}$
(C) $\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{3}{\mathrm{K}}$
(D) $\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{2+\mathrm{K}}{\mathrm{K}}$
[IIT-JEE 2014]
(A) $\frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
(B) $\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{E}_{2}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}}$
(C) $\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{3}{\mathrm{K}}$
(D) $\frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{2+\mathrm{K}}{\mathrm{K}}$
[IIT-JEE 2014]
Ans. (A,D)
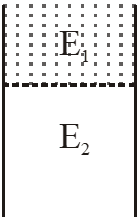 $\mathrm{C}_{1}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0}(\mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\mathrm{With} \text { dielectric })$
$\&$ let $\mathrm{C}_{2}=\frac{\epsilon_{0}(2 \mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\text { without dielectric })$
$\mathrm{C}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}+\frac{\varepsilon_{0} 2 \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}[\mathrm{K}+2]$
$\therefore \frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}+2}{\mathrm{K}}$
As potential difference is same and gap is same.
$\therefore \mathrm{E}_{4}=\mathrm{E}_{2}$
$\therefore \frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
$\mathrm{Q}_{1}=\mathrm{C}_{1} \mathrm{V}, \mathrm{Q}_{2}=\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{V}$
$\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{C}_{1}}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}}{2}$
$\mathrm{C}_{1}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0}(\mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\mathrm{With} \text { dielectric })$
$\&$ let $\mathrm{C}_{2}=\frac{\epsilon_{0}(2 \mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\text { without dielectric })$
$\mathrm{C}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}+\frac{\varepsilon_{0} 2 \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}[\mathrm{K}+2]$
$\therefore \frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}+2}{\mathrm{K}}$
As potential difference is same and gap is same.
$\therefore \mathrm{E}_{4}=\mathrm{E}_{2}$
$\therefore \frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
$\mathrm{Q}_{1}=\mathrm{C}_{1} \mathrm{V}, \mathrm{Q}_{2}=\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{V}$
$\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{C}_{1}}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}}{2}$
 $\mathrm{C}_{1}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0}(\mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\mathrm{With} \text { dielectric })$
$\&$ let $\mathrm{C}_{2}=\frac{\epsilon_{0}(2 \mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\text { without dielectric })$
$\mathrm{C}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}+\frac{\varepsilon_{0} 2 \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}[\mathrm{K}+2]$
$\therefore \frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}+2}{\mathrm{K}}$
As potential difference is same and gap is same.
$\therefore \mathrm{E}_{4}=\mathrm{E}_{2}$
$\therefore \frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
$\mathrm{Q}_{1}=\mathrm{C}_{1} \mathrm{V}, \mathrm{Q}_{2}=\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{V}$
$\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{C}_{1}}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}}{2}$
$\mathrm{C}_{1}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0}(\mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\mathrm{With} \text { dielectric })$
$\&$ let $\mathrm{C}_{2}=\frac{\epsilon_{0}(2 \mathrm{A} / 3)}{\mathrm{d}}(\text { without dielectric })$
$\mathrm{C}=\frac{\mathrm{K} \varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}+\frac{\varepsilon_{0} 2 \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}=\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{A} / 3}{\mathrm{d}}[\mathrm{K}+2]$
$\therefore \frac{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}+2}{\mathrm{K}}$
As potential difference is same and gap is same.
$\therefore \mathrm{E}_{4}=\mathrm{E}_{2}$
$\therefore \frac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=1$
$\mathrm{Q}_{1}=\mathrm{C}_{1} \mathrm{V}, \mathrm{Q}_{2}=\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{V}$
$\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1}}{\mathrm{Q}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{C}_{1}}{\mathrm{C}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{K}}{2}$
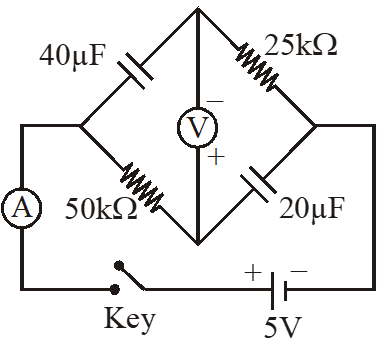
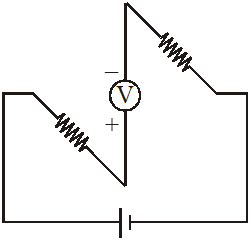
Q. In the circuit shown below, the key is pressed at time t = 0. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true?
(A) The voltmeter displays –5V as soon as the key is pressed, and displays +5V after a long time
(B) The voltmeter will display 0 V at time t = ln 2 seconds
(C) The current in the ammeter becomes 1/e of the initial value after 1 second
(D) The current in the ammeter becomes zero after a long time
 [JEE Advanced 2016]
[JEE Advanced 2016]
 [JEE Advanced 2016]
[JEE Advanced 2016]
Ans. (A,B,C,D)
(A) At t = 0, capacitor acts as short-circuit
$\therefore$
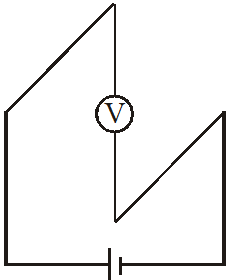 At $\mathrm{t} \rightarrow \infty,$ capacitor acts as open circuit $\&$ no current flows through voltmeter.
$\therefore$
At $\mathrm{t} \rightarrow \infty,$ capacitor acts as open circuit $\&$ no current flows through voltmeter.
$\therefore$
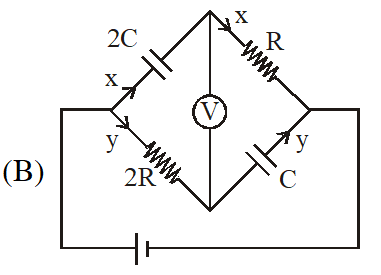 $\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}=2 \mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{y}}=\mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-t / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{2 \mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\mathrm{y} 2 \mathrm{R}+\frac{\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}}{2 \mathrm{C}}$
$=\mathrm{V}\left[1-2 \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right]=0$
(C) $\tau=1$ sec
So by $\mathrm{i}=\mathrm{i}_{0} \mathrm{e}^{-t / \tau}$ current at $\mathrm{t}=1$ sec is $=\mathrm{i}_{0} / \mathrm{e}$
(D) After long time no current flows since both capacitor & voltmeter does not allow.
$\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}=2 \mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{y}}=\mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-t / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{2 \mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\mathrm{y} 2 \mathrm{R}+\frac{\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}}{2 \mathrm{C}}$
$=\mathrm{V}\left[1-2 \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right]=0$
(C) $\tau=1$ sec
So by $\mathrm{i}=\mathrm{i}_{0} \mathrm{e}^{-t / \tau}$ current at $\mathrm{t}=1$ sec is $=\mathrm{i}_{0} / \mathrm{e}$
(D) After long time no current flows since both capacitor & voltmeter does not allow.
 At $\mathrm{t} \rightarrow \infty,$ capacitor acts as open circuit $\&$ no current flows through voltmeter.
$\therefore$
At $\mathrm{t} \rightarrow \infty,$ capacitor acts as open circuit $\&$ no current flows through voltmeter.
$\therefore$

 $\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}=2 \mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{y}}=\mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-t / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{2 \mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\mathrm{y} 2 \mathrm{R}+\frac{\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}}{2 \mathrm{C}}$
$=\mathrm{V}\left[1-2 \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right]=0$
(C) $\tau=1$ sec
So by $\mathrm{i}=\mathrm{i}_{0} \mathrm{e}^{-t / \tau}$ current at $\mathrm{t}=1$ sec is $=\mathrm{i}_{0} / \mathrm{e}$
(D) After long time no current flows since both capacitor & voltmeter does not allow.
$\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}=2 \mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{y}}=\mathrm{CV}\left(1-\mathrm{e}^{-t / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right) \quad \mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{2 \mathrm{R}} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}$
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\mathrm{y} 2 \mathrm{R}+\frac{\mathrm{q}_{\mathrm{x}}}{2 \mathrm{C}}$
$=\mathrm{V}\left[1-2 \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{t} / 2 \mathrm{CR}}\right]=0$
(C) $\tau=1$ sec
So by $\mathrm{i}=\mathrm{i}_{0} \mathrm{e}^{-t / \tau}$ current at $\mathrm{t}=1$ sec is $=\mathrm{i}_{0} / \mathrm{e}$
(D) After long time no current flows since both capacitor & voltmeter does not allow.

Q. In Process 1, the energy stored in the capacitor $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}$ and heat dissipated across resistance $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}$ are related by :-
(A) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}$
(B) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{c}}=2 \mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}$
(C) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}$
(D) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}} \ln 2$
[JEE Advanced 2017]
Ans. (A)
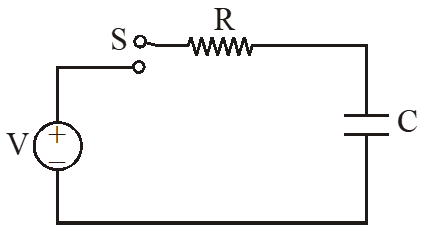 When switch is closed for a very long time capacitor will get fully charged & charge on capacitor will be q = CV
Energy stored in capacitor $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2} \quad \ldots$ (i)
Work done by battery $(\mathrm{W})=\mathrm{Vq}=\mathrm{VCV}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}$
dissipated across resistance $\in_{\mathrm{D}}=(\text { work done by battery })-$ (energy store)
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}-\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}$ ...(ii)
from (i) $\&($ ii )
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}$
When switch is closed for a very long time capacitor will get fully charged & charge on capacitor will be q = CV
Energy stored in capacitor $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2} \quad \ldots$ (i)
Work done by battery $(\mathrm{W})=\mathrm{Vq}=\mathrm{VCV}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}$
dissipated across resistance $\in_{\mathrm{D}}=(\text { work done by battery })-$ (energy store)
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}-\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}$ ...(ii)
from (i) $\&($ ii )
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}$
 When switch is closed for a very long time capacitor will get fully charged & charge on capacitor will be q = CV
Energy stored in capacitor $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2} \quad \ldots$ (i)
Work done by battery $(\mathrm{W})=\mathrm{Vq}=\mathrm{VCV}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}$
dissipated across resistance $\in_{\mathrm{D}}=(\text { work done by battery })-$ (energy store)
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}-\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}$ ...(ii)
from (i) $\&($ ii )
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}$
When switch is closed for a very long time capacitor will get fully charged & charge on capacitor will be q = CV
Energy stored in capacitor $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2} \quad \ldots$ (i)
Work done by battery $(\mathrm{W})=\mathrm{Vq}=\mathrm{VCV}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}$
dissipated across resistance $\in_{\mathrm{D}}=(\text { work done by battery })-$ (energy store)
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{CV}^{2}-\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}^{2}$ ...(ii)
from (i) $\&($ ii )
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{C}}$
Q. In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance $E_{D}$ is :-
(A) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\frac{1}{3}\left(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}\right)$
(B) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=3\left(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}\right)$
(C) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}$
(D) $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=3 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}$
[JEE Advanced 2017]
Ans. (A)
For process (1)
Charge on capacitor $=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3}$
energy stored in capacitor $=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{C} \frac{\mathrm{V}_{0}^{2}}{9}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
work done by battery $=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3} \times \frac{\mathrm{V}}{3}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{9}$
Heat loss $=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{9}-\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
For process (2)
Charge on capacitor $=\frac{2 \mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3}$
Extra charge flow through battery $=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3}$
Work done by battery $: \frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3} \cdot \frac{2 \mathrm{V}_{0}}{3}=\frac{2 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{9}$
Final energy store in capacitor : $\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{C}\left(\frac{2 \mathrm{V}_{0}}{3}\right)^{2}=\frac{4 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
energy store in process $2: \frac{4 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}-\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}=\frac{3 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
Heat loss in process (2) = work done by battery in process (2) – energy store in capacitor process (2)
$=\frac{2 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{9}-\frac{3 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
For process (3)
Charge on capacitor $=\mathrm{CV}_{0}$
extra charge flow through battery : $\mathrm{CV}_{0}-\frac{2 \mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3}$
work done by battery in this process : $\left(\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}}{3}\right)\left(\mathrm{V}_{0}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{C} \mathrm{V}_{0}^{2}}{3}$
find energy store in capacitor $: \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}$
energy stored in this process : $\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}-\frac{4 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}=\frac{5 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
heat loss in process ( 3)$: \frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{3}-\frac{5 \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}$
Now total heat loss $\left(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}\right): \frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}+\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}+\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{18}=\frac{\mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}}{6}$
final energy store in capacitor : $\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}$
so we can say that $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{D}}=\frac{1}{3}\left(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{CV}_{0}^{2}\right)$
Q. Three identical capacitors $\mathrm{C}_{1}, \mathrm{C}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{C}_{3}$ have a capacitance of $1.0 \mu \mathrm{F}$ each and they are uncharged initially. They are connected in a circuit as shown in the figure and $\mathrm{C}_{1}$ is then filled completely with a dielectric material of relative permittivity $\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}$. The cell electromotive force (emf) $\mathrm{V}_{0}=8 \mathrm{V}$ . First the switch $\mathrm{S}_{1}$ is closed while the switch $\mathrm{S}_{2}$ is kept open. When the capacitor $\mathrm{C}_{3}$ is fully charged, $\mathrm{S}_{1}$ is opened and $\mathrm{S}_{2}$ is closed simultaneously. When all the capacitors reach equilibrium, the charge on $\mathrm{C}_{3}$ is found to be $5 \mu \mathrm{C}$. The value of $\in_{\mathbf{I}}$.
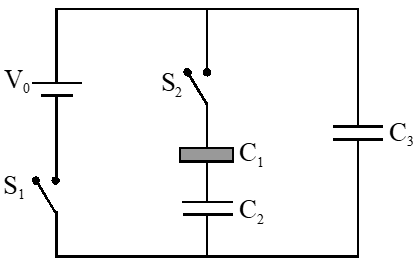 [JEE Advanced 2018]
[JEE Advanced 2018]
 [JEE Advanced 2018]
[JEE Advanced 2018]
Ans. 1.5
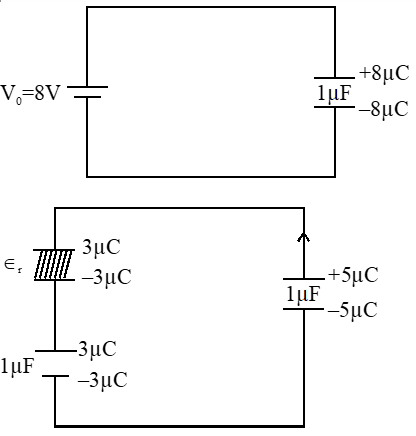 Applying loop rule
$\frac{5}{1}-\frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}-\frac{3}{1}=0 \quad \frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}=2$
$\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}=1.50$
Applying loop rule
$\frac{5}{1}-\frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}-\frac{3}{1}=0 \quad \frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}=2$
$\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}=1.50$
 Applying loop rule
$\frac{5}{1}-\frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}-\frac{3}{1}=0 \quad \frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}=2$
$\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}=1.50$
Applying loop rule
$\frac{5}{1}-\frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}-\frac{3}{1}=0 \quad \frac{3}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}}=2$
$\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}=1.50$
